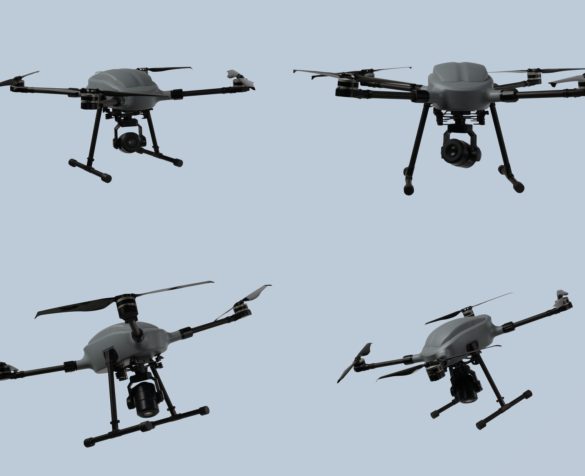
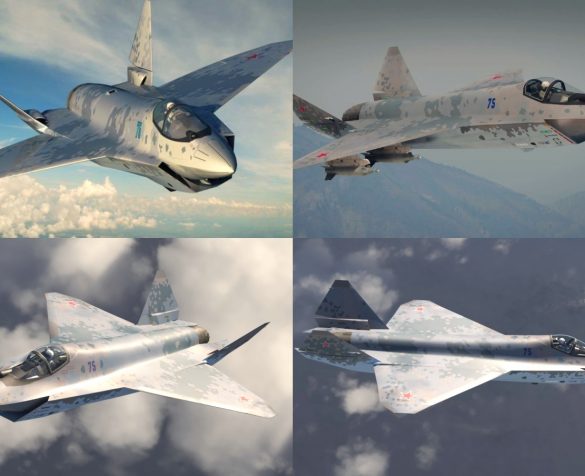
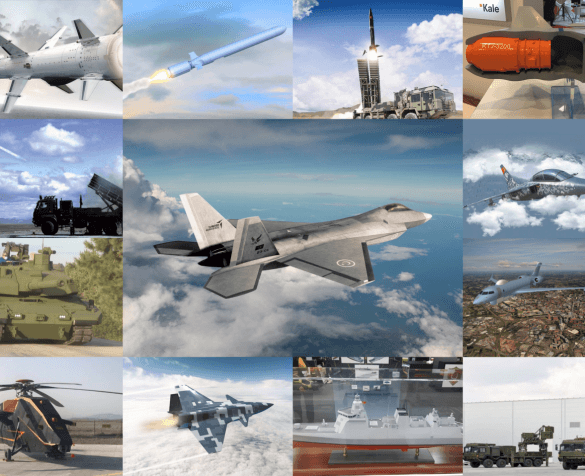
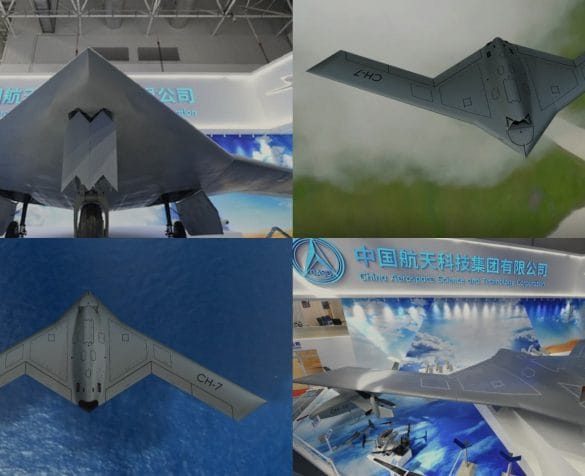
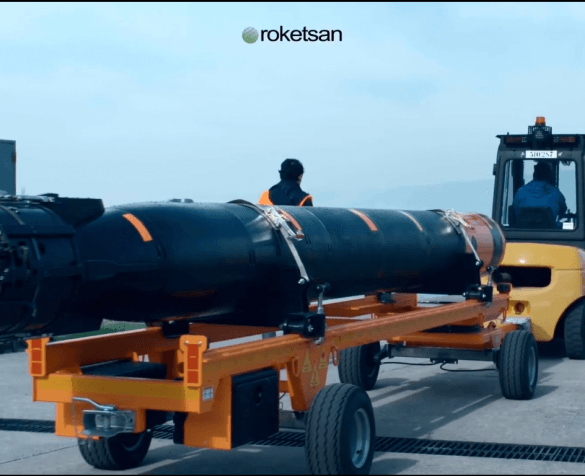
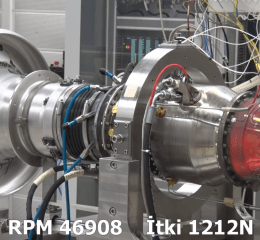
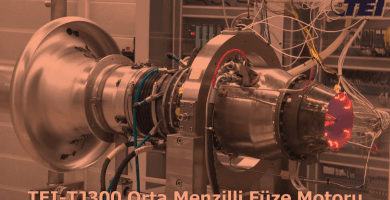
Türkiye’nin Turbofan ve Turbojet Motor Projeleri
Temmuz 16, 2022
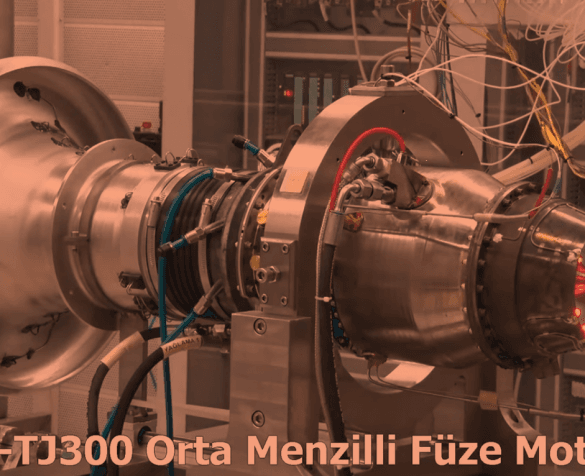
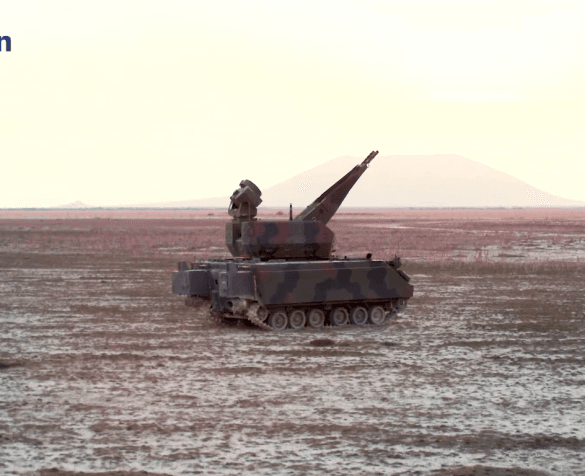
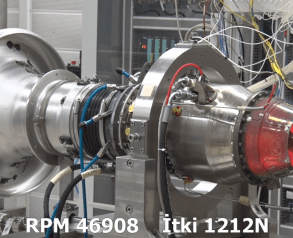
Türkiye’nin savunma ve havacılık endüstrisindeki en büyük eksikliklerinden biri olan motorlar alanında TUSAŞ Motor Sanayii …